Blower System Integration for Wastewater Aeration Applications
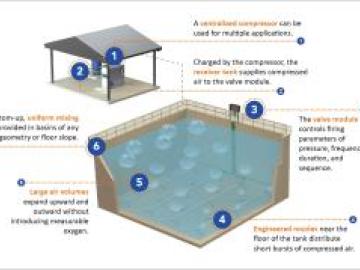
The overall wastewater treatment process is complex, and each step is integral to ensuring water is properly purified. Effluent ends up in the plants, containing substances that must be removed before the water can be properly cleaned and returned for use. The range of potential contaminants is almost endless and can include food, pulp, waste, or other substances. Afterwards, the water requires further scrubbing, with the aid of bacteria. It is in this part of the process that compressed air (ideally provided by energy-efficient rotary lobe blowers) plays a vital role.